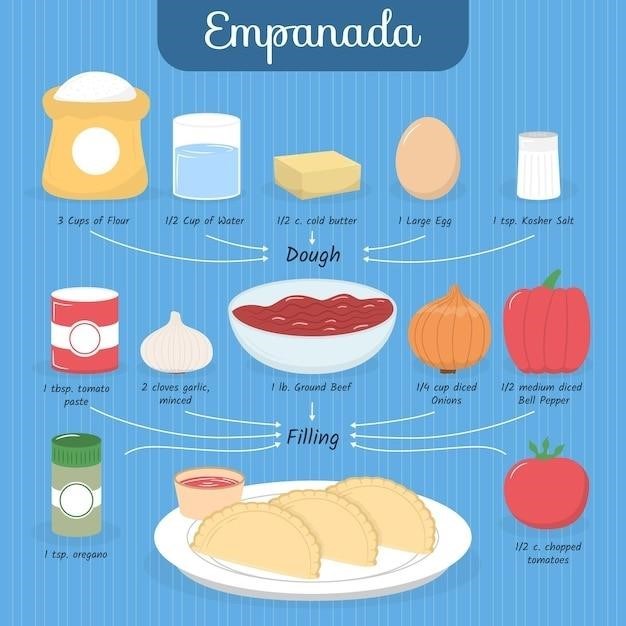
Jimmy Dean Sausage Egg and Cheese Biscuit sandwiches are a quick and easy breakfast option. They can be cooked in the microwave‚ oven‚ or air fryer. Here are some tips for cooking these sandwiches to perfection.
Microwave Instructions
Microwaving is the quickest and easiest way to cook a Jimmy Dean Sausage Egg and Cheese Biscuit. However‚ it’s important to follow the specific instructions for your microwave to ensure the sandwich is cooked evenly and safely. Here’s a general guide⁚
- Prepare⁚ Remove the sandwich from its wrapper and wrap it in a paper towel. This helps to prevent the sandwich from becoming soggy and ensures even cooking.
- Defrost (if needed)⁚ If your sandwich is frozen‚ defrost it on a low power setting in the microwave for 90 seconds. Turn the sandwich over halfway through the defrosting process.
- Heat⁚ Microwave the sandwich on high power for 55 seconds. However‚ this time can vary depending on the power of your microwave. Always check the sandwich for doneness and adjust the cooking time accordingly. The sandwich should be heated through and the cheese should be melted.
- Let stand⁚ Allow the sandwich to stand for 1 minute before enjoying to ensure it is safe to eat. The sandwich will continue to cook slightly as it rests.
Remember‚ microwave ovens vary in wattage‚ so always monitor the cooking process. Adjust the time if necessary. The sandwich should be hot and the cheese melted.
Oven Instructions
For a slightly crispier biscuit and a more evenly cooked sandwich‚ baking in the oven is a great option. Here’s how to achieve the perfect oven-baked Jimmy Dean Sausage Egg and Cheese Biscuit⁚
- Preheat⁚ Preheat your oven to 350°F (175°C). This ensures the sandwich cooks thoroughly and the cheese melts evenly.
- Prepare⁚ Remove the sandwich from its wrapper; To prevent the sandwich from separating during baking‚ consider separating it between the sausage and the egg‚ wrapping each part individually in foil.
- Bake⁚ Place the sandwich on a baking sheet and bake for 20-25 minutes. This allows the biscuit to brown slightly and the filling to heat through.
- Check Doneness⁚ Check the sandwich after 20 minutes. The biscuit should be golden brown and the cheese fully melted. If it’s not quite done‚ bake for a few more minutes.
- Rest⁚ Allow the sandwich to rest for a few minutes before enjoying to ensure it’s safe to eat. The filling will continue to cook slightly as it rests.
Baking offers a more traditional way to heat your Jimmy Dean Sausage Egg and Cheese Biscuit and allows for a bit more control over the browning and crispness of the biscuit.
Air Fryer Instructions
For a crispy biscuit and a perfectly heated Jimmy Dean Sausage Egg and Cheese Biscuit‚ air frying is a convenient and efficient option. Follow these steps to achieve a delicious and crispy breakfast sandwich⁚
- Prepare⁚ Remove the sandwich from its wrapper. To avoid the sandwich separating during cooking‚ consider separating it between the sausage and the egg‚ wrapping each part individually in foil.
- Preheat⁚ Preheat your air fryer to 370°F (190°C). This ensures the biscuit becomes crispy and the filling heats through evenly.
- Cook⁚ Place the sandwich in the air fryer basket and cook for 13 minutes. The air fryer’s circulating hot air helps to create a crispy biscuit and ensures the filling is cooked through.
- Check Doneness⁚ After 13 minutes‚ check the sandwich. The biscuit should be golden brown and the cheese fully melted. If the biscuit isn’t quite crispy enough‚ cook for a few more minutes.
- Rest⁚ Allow the sandwich to rest for a few minutes before enjoying to ensure it’s safe to eat. The filling will continue to cook slightly as it rests.
Air frying provides a fast and easy way to cook your Jimmy Dean Sausage Egg and Cheese Biscuit‚ offering a crispy texture and a delicious‚ heated breakfast sandwich.
Microwave Oven Variations
While the standard microwave instructions provide a quick and easy way to heat your Jimmy Dean Sausage Egg and Cheese Biscuit‚ some variations can enhance the cooking process and result in a more satisfying breakfast. Here are a few options to try⁚
- Power Level Adjustment⁚ For a less powerful microwave (less than 1100 watts)‚ try cooking the sandwich on a lower power level (e.g.‚ 30%) for 1.5 minutes‚ then switching to full power for 50-55 seconds. This helps ensure the biscuit is heated through without becoming rubbery.
- Paper Towel Wrap⁚ Wrapping the sandwich in a paper towel before microwaving can help absorb excess moisture and prevent the biscuit from becoming soggy. This technique is particularly useful for microwaves that have a tendency to generate excess steam.
- Defrosting⁚ For a frozen Jimmy Dean Sausage Egg and Cheese Biscuit‚ defrosting it in the microwave on a low power setting for 90 seconds before heating can help ensure even cooking and prevent a cold center. Turn the sandwich over halfway through the defrosting process.
- Let it Rest⁚ After microwaving‚ let the sandwich rest for about a minute before enjoying. This allows the filling to continue cooking slightly and the biscuit to become less steamy‚ making for a more enjoyable eating experience.
Experimenting with these variations can help you find the best way to cook your Jimmy Dean Sausage Egg and Cheese Biscuit in your microwave‚ ensuring a delicious and satisfying breakfast.
Commercial Microwave Instructions
If you’re using a commercial microwave‚ such as those found in restaurants or food service settings‚ the cooking instructions for Jimmy Dean Sausage Egg and Cheese Biscuits may differ slightly from those for home microwaves. Here’s a general guide for heating these sandwiches in a commercial microwave⁚
- Remove Wrapper⁚ Start by removing the plastic wrapper from the sandwich. This allows for more even heating and prevents the wrapper from potentially melting or catching fire.
- Wrap in Paper Towel⁚ Wrap the sandwich in a paper towel to help absorb excess moisture and prevent the biscuit from becoming soggy. This is especially important in commercial microwaves‚ which often have higher power levels.
- Heat for 55 Seconds⁚ Place the wrapped sandwich in the commercial microwave and heat it on high for 55 seconds. Adjust the heating time as needed based on the wattage of the microwave and the desired level of doneness.
- Caution⁚ Product Will Be Hot⁚ After heating‚ carefully remove the sandwich from the microwave using oven mitts or a heat-resistant potholder. The sandwich will be very hot‚ so handle it with caution.
Always check the specific instructions provided by the manufacturer of the commercial microwave for optimal heating results. These general instructions are a good starting point‚ but adjustments may be necessary depending on the individual appliance and the desired level of doneness.
Tips and Tricks
While Jimmy Dean Sausage Egg and Cheese Biscuits are designed for convenience‚ a few simple tips and tricks can elevate your breakfast experience. These suggestions can help you achieve optimal texture‚ flavor‚ and overall satisfaction.
- Separate and Wrap⁚ For a more even cook and to prevent the ingredients from separating during heating‚ consider separating the sandwich between the egg and sausage. Wrap each half individually in foil‚ then place them on a baking sheet for oven cooking or in the air fryer. This helps prevent the biscuit from becoming soggy and ensures that the sausage and egg are cooked thoroughly.
- Air Fryer Delight⁚ For a crispier biscuit and a touch of added texture‚ consider cooking your Jimmy Dean Sausage Egg and Cheese Biscuit in an air fryer. Preheating the air fryer to 370 degrees Fahrenheit and cooking for 13 minutes typically yields a delicious result.
- Experiment with Cheese⁚ If you’re seeking a flavor twist‚ try replacing the standard cheese with a different variety. Pepper jack‚ Swiss‚ or even a blend of cheeses can add a unique dimension to your breakfast sandwich.
- Beyond the Biscuit⁚ Jimmy Dean offers a range of breakfast sandwiches beyond the classic biscuit variety. Explore options like bagels or English muffins for a change of pace;
Remember‚ these tips are suggestions to enhance your breakfast experience. Feel free to experiment and find your perfect way to enjoy Jimmy Dean Sausage Egg and Cheese Biscuits.

Safety Precautions
While Jimmy Dean Sausage Egg and Cheese Biscuits are a delicious and convenient breakfast option‚ it’s important to prioritize safety when preparing them. Here are some key safety precautions to keep in mind⁚
- Handle with Care⁚ Always handle the frozen biscuits with care. Their surface can be quite cold‚ so avoid touching them directly for extended periods. Use oven mitts or pot holders when removing them from the oven or air fryer;
- Microwave Caution⁚ When cooking in the microwave‚ it’s essential to be mindful of the heat generated. The sandwich will be extremely hot after cooking. Use caution when removing it from the microwave and allow it to cool slightly before consuming. Avoid touching the sandwich directly until it has reached a safe temperature.
- Oven Safety⁚ When using the oven‚ ensure that the baking sheet is placed in the center rack and not too close to the heating elements. This prevents the biscuit from burning and helps ensure even cooking. Also‚ monitor the cooking time closely and remove the sandwich promptly once it is cooked through.
- Air Fryer Supervision⁚ During air fryer cooking‚ always keep a close eye on the sandwich. The air fryer can heat up quickly‚ so it’s important to avoid leaving it unattended. Check the sandwich frequently to ensure it doesn’t burn or become overcooked.
By following these safety precautions‚ you can enjoy your Jimmy Dean Sausage Egg and Cheese Biscuits with peace of mind‚ knowing that you are taking steps to prevent potential accidents and burns.
Storage and Handling
Proper storage and handling of Jimmy Dean Sausage Egg and Cheese Biscuits are crucial for maintaining their quality and freshness. Here’s a guide to ensure you get the most out of your breakfast sandwiches⁚
- Frozen Storage⁚ Keep the biscuits frozen until ready to cook. Store them in their original packaging in the freezer for up to the date indicated on the package. Avoid thawing and refreezing‚ as this can affect the texture and taste.
- Refrigerator Storage (After Thawing)⁚ If you have thawed the biscuits‚ they can be stored in the refrigerator for up to 2 days. Wrap them tightly in plastic wrap or aluminum foil to prevent freezer burn and maintain moisture.
- Defrosting⁚ If you need to defrost the biscuits‚ the best method is to transfer them from the freezer to the refrigerator overnight. Avoid thawing at room temperature‚ as this can lead to bacterial growth.
- Handling Precautions⁚ Always wash your hands thoroughly with soap and water before handling the biscuits. Use clean utensils and surfaces to prevent cross-contamination. If you’re using a microwave-safe dish‚ ensure it’s clean and free from any residue.
By adhering to these storage and handling guidelines‚ you can ensure that your Jimmy Dean Sausage Egg and Cheese Biscuits remain fresh‚ flavorful‚ and safe to consume.
Nutritional Information
Jimmy Dean Sausage Egg and Cheese Biscuits provide a quick and convenient breakfast option‚ but it’s essential to be aware of their nutritional content. Here’s a breakdown of the typical nutritional information for a single serving‚ which is one sandwich⁚
- Calories⁚ Approximately 350-400 calories.
- Fat⁚ Around 20-25 grams of fat‚ including saturated fat‚ monounsaturated fat‚ and polyunsaturated fat.
- Cholesterol⁚ High in cholesterol‚ typically around 100-150 milligrams.
- Sodium⁚ High in sodium‚ usually around 800-900 milligrams.
- Carbohydrates⁚ Approximately 30-35 grams of carbohydrates‚ including sugar.
- Protein⁚ Around 15-20 grams of protein.
It’s important to note that these figures may vary slightly depending on the specific variety and preparation method. It’s always recommended to check the nutritional label on the product packaging for the most accurate information. As with any processed food‚ moderation is key. If you’re concerned about your sodium intake‚ you may want to consider reducing your consumption of these sandwiches or choosing alternative breakfast options that are lower in sodium.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some common questions people have about cooking Jimmy Dean Sausage Egg and Cheese Biscuits⁚
- How long should I microwave a Jimmy Dean sausage‚ egg‚ and cheese biscuit? Microwave cooking times vary depending on the wattage of your microwave. However‚ a general guideline is to microwave for 45-55 seconds on high power. Always check the product packaging for specific instructions and adjust cooking time as needed.
- Can I cook a Jimmy Dean sausage‚ egg‚ and cheese biscuit in the air fryer? Yes‚ you can cook these sandwiches in an air fryer. Wrap the sandwich in foil to prevent it from drying out and cook at 370°F for 13-15 minutes. Adjust cooking time based on your air fryer’s wattage and desired level of crispiness.
- How do I reheat a Jimmy Dean sausage‚ egg‚ and cheese biscuit? You can reheat these sandwiches in the microwave or oven. For the microwave‚ simply heat for 30-45 seconds on high power. For the oven‚ preheat to 350°F and bake for 10-15 minutes. Ensure the sandwich is heated through before enjoying.
- Can I freeze Jimmy Dean sausage‚ egg‚ and cheese biscuits? Yes‚ you can freeze these sandwiches. Wrap them tightly in plastic wrap or aluminum foil to prevent freezer burn and store in the freezer for up to 3 months. To thaw‚ remove from the freezer and let sit at room temperature for several hours or thaw overnight in the refrigerator. Reheat as desired.
If you have any other questions about cooking Jimmy Dean Sausage Egg and Cheese Biscuits‚ consult the product packaging or visit the Jimmy Dean website for additional information.
Alternative Cooking Methods
While the microwave‚ oven‚ and air fryer are popular methods for cooking Jimmy Dean Sausage Egg and Cheese Biscuits‚ there are a few other alternatives you can explore for a different culinary experience.
- Skillet Cooking⁚ For a crispy exterior and a warm‚ gooey interior‚ try cooking your biscuit sandwich in a skillet over medium heat. Heat a tablespoon of butter or oil in the skillet‚ then carefully place the sandwich in the pan. Cook for 2-3 minutes per side‚ or until golden brown and heated through. Be careful not to overcook‚ as the biscuit can become too hard.
- Grill Cooking⁚ If you’re feeling adventurous‚ try grilling your Jimmy Dean Sausage Egg and Cheese Biscuit. Preheat your grill to medium heat. Place the sandwich on the grill and cook for 2-3 minutes per side‚ or until heated through and slightly charred. The grill marks will add a unique flavor to your breakfast sandwich.
- Toaster Oven Cooking⁚ For a more compact and efficient cooking method‚ a toaster oven can be a great alternative to the full-sized oven. Preheat your toaster oven to 350°F and place the sandwich inside on a baking sheet. Cook for 10-15 minutes‚ or until heated through and slightly golden brown.
Remember to always adjust cooking times based on the power of your appliance and your desired level of doneness. Experiment with these alternative methods to find your favorite way to enjoy a delicious Jimmy Dean Sausage Egg and Cheese Biscuit.